MCP Node Usage Guide #
Overview #
The MCP (Model Context Protocol) node allows you to integrate external services and APIs into your WordPress AI workflows. It supports both preset services (Slack, GitHub, Gmail, etc.) and custom MCP servers.
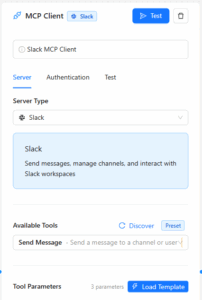
Setting Up MCP Nodes in Workflows #
1. Basic Configuration #
- Node Name: Give your MCP node a descriptive name
- Server Type: Choose from preset services or “Custom”
- Authentication: Enter required credentials (API keys, tokens, etc.)
- Tool Selection: Select the specific action/tool to execute
- Parameters: Configure the parameters for your selected tool
2. Using Input Tags #
MCP nodes support dynamic input from other nodes using tags:
[[node-id]] - Get full output from a node
[[field] from node-id] - Get specific field from a node
Examples: #
- Send Slack message with AI-generated content:
Channel: #general Text: [[aiModel-1]] - Create GitHub issue from form submission:
Title: [[subject] from trigger-1] Body: [[description] from trigger-1]
3. Preset Service Examples #
Slack Integration #
{
"serverType": "slack",
"selectedTool": "send_message",
"connectionConfig": {
"bot_token": "xoxb-your-bot-token"
},
"toolParameters": [
{"name": "channel", "value": "#notifications"},
{"name": "text", "value": "New workflow completed: [[trigger-1]]"}
]
}
GitHub Integration #
{
"serverType": "github",
"selectedTool": "create_issue",
"connectionConfig": {
"access_token": "ghp_your_token"
},
"toolParameters": [
{"name": "repo", "value": "owner/repository"},
{"name": "title", "value": "[[title] from humanInput-1]"},
{"name": "body", "value": "[[content] from aiModel-1]"}
]
}
Gmail Integration #
{
"serverType": "gmail",
"selectedTool": "send_email",
"connectionConfig": {
"access_token": "your_oauth_token"
},
"toolParameters": [
{"name": "to", "value": "[[email] from trigger-1]"},
{"name": "subject", "value": "Your AI-Generated Report"},
{"name": "body", "value": "[[output-1]]"}
]
}
4. Custom MCP Server Configuration #
For custom MCP servers, you need to provide:
HTTP/HTTPS Server #
{
"serverType": "custom",
"customServerConfig": {
"name": "My Custom API",
"connectionType": "http",
"endpoint": "https://api.example.com",
"authFields": [
{"key": "X-API-Key", "value": "your-api-key"}
]
},
"selectedTool": "custom_action",
"toolParameters": [
{"name": "input", "value": "[[aiModel-1]]"}
]
}
Local Process (stdio) #
{
"serverType": "custom",
"customServerConfig": {
"name": "Local Python Script",
"connectionType": "stdio",
"command": "python",
"args": ["/path/to/mcp_server.py"]
},
"selectedTool": "process_data",
"toolParameters": [
{"name": "data", "value": "[[parser-1]]"}
]
}
Common Use Cases #
1. Notification Workflow #
Trigger → AI Model → MCP (Slack) → Output
- Form submission triggers workflow
- AI generates summary
- MCP sends Slack notification
- Output saves to database
2. Content Publishing Workflow #
RSS → AI Model → MCP (GitHub) → MCP (Gmail)
- RSS feed provides new content
- AI rewrites/summarizes
- MCP creates GitHub issue
- MCP sends email notification
3. Data Processing Workflow #
API Call → Parser → MCP (PostgreSQL) → Output
- Fetch data from API
- Parse/transform data
- Store in PostgreSQL via MCP
- Display results
Working with Complex Parameters #
JSON Arrays #
Some tools expect JSON arrays. Format them as strings:
Query Texts: ["search term 1", "search term 2"]
Documents: [{"id": 1, "text": "content"}, {"id": 2, "text": "more"}]
Nested Objects #
For complex data structures:
Data: {"user": {"name": "[[name] from trigger-1]", "email": "[[email] from trigger-1]"}}
Dynamic Lists #
Use AI to generate formatted lists:
Attendees: [[aiModel-1]] // AI outputs: "email1@example.com, email2@example.com"
Error Handling #
- Authentication Errors: Double-check API keys and tokens
- Parameter Errors: Ensure required parameters are provided
- Format Errors: Validate JSON syntax for array/object parameters
- Connection Errors: Verify server endpoints and network access
Best Practices #
- Test First: Always test your MCP configuration before adding to production workflows
- Use Templates: Start with tool templates and modify as needed
- Secure Credentials: Store sensitive tokens in WordPress options, not in workflow JSON
- Error Recovery: Add condition nodes after MCP nodes to handle failures
- Rate Limiting: Be aware of API rate limits for external services
Troubleshooting #
MCP Node Not Executing #
- Check execution logs in WordPress admin
- Verify all required parameters are filled
- Test the connection using the “Test” button
Invalid Response #
- Check the API documentation for expected response format
- Verify authentication is working
- Look for error messages in the execution details
Parameter Issues #
- Ensure JSON is properly formatted
- Check that input tags are resolving correctly
- Verify data types match API expectations


