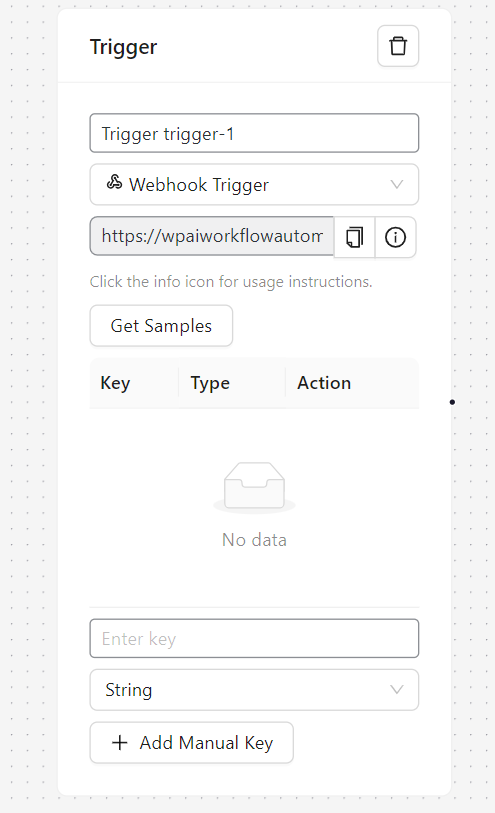
The Webhook Trigger node allows your workflow to be initiated by external HTTP POST requests, enabling integration with a wide range of third-party services and APIs.
Key features:
- Dynamic Payload Handling: The trigger can adapt to different payload structures.
- Key Mapping: Users can define how incoming data should be mapped to workflow variables.
- Data Sampling: There’s a “Get Samples” feature that allows users to capture and analyze the structure of incoming webhook data.
- Manual Key Addition: Users can manually add expected keys and specify their data types (string, number, boolean).
- Nested Data Support: The webhook can handle complex, nested JSON structures. Users can access nested data using a / notation or similar system in subsequent nodes.
Configuration #
- Add a Webhook Trigger node to your workflow.
- A unique webhook URL will be automatically generated.
Using the Webhook #
- Send a POST request to the generated URL to trigger your workflow.
- The data sent in the POST request body will be available in your workflow.
Data Handling #
- Incoming data is parsed automatically (supports JSON and form-encoded data).
- Access webhook data in subsequent nodes using tags:
[Input from webhook-node-id]for the entire payload[[specific_field] from webhook-node-id]for individual fields
Security #
- Each webhook URL contains a unique key for basic security.
- For additional security, consider using API key validation in your workflow.
Use Cases #
- Integrate with external services like Zapier or IFTTT
- Receive data from custom applications or scripts
- Receive data from other WordPress plugins or automation tools such as GravityFlow, Uncanny Automator, AutomatorWP, etc.
- Create API endpoints for your WordPress site


